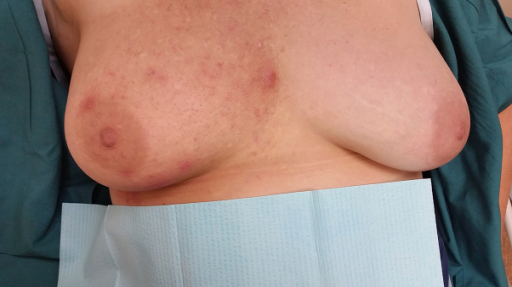
Radiation therapy-induced skin reactions
Radiation dermatitis is a common side effect of radiation therapy; a combination of radiation injury (ionizing radiation) and the inflammatory response that occurs. Although the skin is not often the primary target, the RT beams must pass through the skin to treat the underlying breast or chest wall. Radiation dermatitis may be evident one to four weeks after beginning treatment and can persist for several weeks post-treatment.
Radiation dermatitis grading criteria (adapted SCoR Radiation Dermatitis Guidelines April 2020)
Grade 0 |
Grade 1 |
Grade 2a |
Grade 2b |
Grade 3 |
No visible change to the skin |
Faint or bright erythema Mild tightness of the skin and mild itching may occur |
Tender or bright erythema Skin may feel tighter, itchy and/or sore. |
Patchy moist desquamation Areas where skin has broken down can be seen. Yellow/pale green exudate may be visible on the surface. Soreness and oedema are evident. |
Confluent moist desquamation More pronounced areas of broken skin can be seen. Yellow/pale green exudate are visible. Soreness and oedema are evident. |
Aims of Care |
||||
To promote hydrated skin and maintain skin integrity To promote comfort |
Reduce risk of complications of further trauma and infection To promote comfort |
|||
Guidance |
||||
Moisturise: Advise patient to continue moisturising with preferred products. If the patient is not already using a moisturiser, advise them to start. Encourage self-care Discuss self-care guidelines and ensure that the patient has sources of information to refer to. Steroid or cortisone creams: Consider / prescribe steroid or cortisone creams following advice from the specialist radiation oncology team. Contraindications for using these creams are broken skin or signs of infection. Analgesia Ensure adequate analgesia is prescribed as required If the skin breaks: Advise patients to discontinue using any cream and provide with appropriate dressings. If there are signs of infections, seek further advice from the specialist radiation oncology team. |
Moisturise: Continue to apply moisturiser to skin within the treatment field that is still intact. Encourage self-care: Discuss self-care, e.g. dress comfortably (loose fitting and preferably cotton), avoid underwire bras, when showering or bathing use warm water, avoid strong soaps with fragrance. Analgesia: Ensure adequate analgesia is prescribed for the patient as required. Dressings: Use appropriate dressings / products on broken skin, e.g. non-adhesive, silicone low adhesion. Infection screening: If signs of infection take a swab and if infection indicated, commence antibiotic treatment. |
|||
If you are unsure, seek advice from the specialist radiation oncology team |
||||